- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Why is the system pressure normal but the cylinder thrust insufficient?
2025-09-03
Introduction
During the operation of the hydraulic system, operators often encounter a confusing problem: the pressure gauge shows that the system pressure is normal, but the hydraulic cylinder cannot output enough thrust. This fault not only affects production efficiency, but may also hide greater equipment hidden dangers. This article will analyze the cause of this phenomenon from a professional perspective and provide a systematic solution.
1. Fault mechanism analysisThe normal pressure of the hydraulic system only indicates that the output pressure of the power source has reached the rated value, but the output thrust of the cylinder depends on the following two key factors:
Thrust = pressure × effective working area
Therefore, normal system pressure cannot guarantee that the cylinder will generate sufficient output thrust.
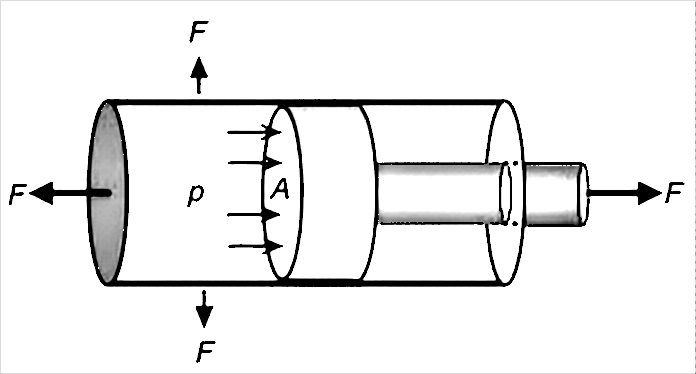
2. Analysis of main causes
(1) Internal leakage of the hydraulic system
l Internal leakage of the cylinder:
Wear or damage of the piston seal will cause the high-pressure chamber to leak into the low-pressure chamber, reducing the effective working pressure. Scratches or wear on the inner wall of the cylinder exceeding the allowable range will also cause internal leakage. In addition, excessive clearance between the piston and the cylinder will also cause leakage problems. In addition to cylinder scratches, slight bending of the piston rod may also cause eccentric wear of the piston, accelerating seal damage and internal leakage.
l Internal leakage of the valve group:
Wear of the reversing valve core causes internal leakage to exceed the allowable value. Hydraulic lock or balance valve sealing is not tight, which will cause the pressure holding function to fail. Overload relief valve setting value is too low or seal failure can also cause pressure loss.
(2) Abnormal mechanical resistance
The deviation of the cylinder installation coaxiality exceeds the allowable range, which will increase the movement resistance. Over-tightening of the guide rail or slider and poor lubrication will increase the friction coefficient. Mechanical interference or sticking of the actuator will also consume effective thrust.
(3) Pressure measurement error
Improper selection of pressure detection point cannot truly reflect the working pressure. Incorrect setting of remote pressure regulating valve or pressure reducing valve will cause the actual working pressure to be lower than the displayed value. Insufficient or damaged pressure gauge will also cause reading error.
(4) Failure of sealing system
Improper selection of seals and mismatch with working medium or working conditions will shorten the service life. Incorrect installation of seals or initial damage will lead to early failure. Oil contamination exceeding NAS Level 9 will accelerate seal wear.
(5) Excessive return oil back pressure
A clogged return oil filter will increase return oil resistance. Insufficient return oil line diameter or too many elbows will produce a throttling effect. Insufficient flow capacity of the reversing valve will also cause increased back pressure.
3. Systematic troubleshooting process (1) Pressure verification
Install a calibrated pressure gauge directly at the oil inlet of the cylinder to measure the actual working pressure. Compare the difference between the system pressure and the working pressure. Under normal circumstances, the difference should not exceed 0.5 MPa.
(2) Leak detection
Perform a pressure holding test: Move the cylinder to the end of the stroke, maintain the rated pressure for 5 minutes, and record the pressure drop. Normal system pressure drop should not exceed 10% of the rated value.
(3) Mechanical inspection
Use a laser alignment instrument to check the coaxiality of the cylinder installation. The deviation should be controlled within 0.05 mm/m. Manually test the actuator movement resistance. Abnormal resistance often indicates a mechanical problem.
(4) Seal detection
Disassemble and check the integrity of the seal and measure whether the size of the seal groove meets the standard. Use a particle size detector to analyze the oil contamination to ensure that it meets the NAS level 9 standard or above.
(5) Return oil detection
Install a pressure gauge on the return oil line to measure the back pressure value, which should normally be lower than 0.3MPa. Check the filter pressure differential indication and replace the blocked filter element in time.
Summary
The fault of "normal system pressure but insufficient cylinder thrust" is essentially a problem in the effective transmission of pressure or efficient conversion of thrust. The troubleshooting process is like a detective solving a case, and it is necessary to follow a scientific logical chain:
(1) The first principle: trust data, not intuition. By directly measuring the pressure at the cylinder port, the actual working pressure is obtained. This is the only gold standard to distinguish "insufficient pressure" from "failure of thrust conversion".
(2) Core idea: from simple to complex, from outside to inside. Prioritize the external mechanical resistance and installation problems, and then conduct complex hydraulic system internal leakage detection, which can achieve twice the result with half the effort.
(3) Key method: pressure verification and pressure holding test. These two steps are the most direct and effective means of diagnosing hydraulic faults, accurately pinpointing whether the fault lies within the valve block, cylinder, or actuator.
In summary, for this type of fault, follow the three-step troubleshooting process: "Verify actual pressure → Check mechanical resistance → Test for system leaks." This systematic diagnosis not only ensures rapid resumption of production but also fundamentally eliminates equipment hazards, ensuring stable and efficient operation of the hydraulic system.




